发布时间:2023-05-11 点击次数:
所属单位:China University of Mining and Technology
发表刊物:Physics of Fluids (JCR Q1 Top)
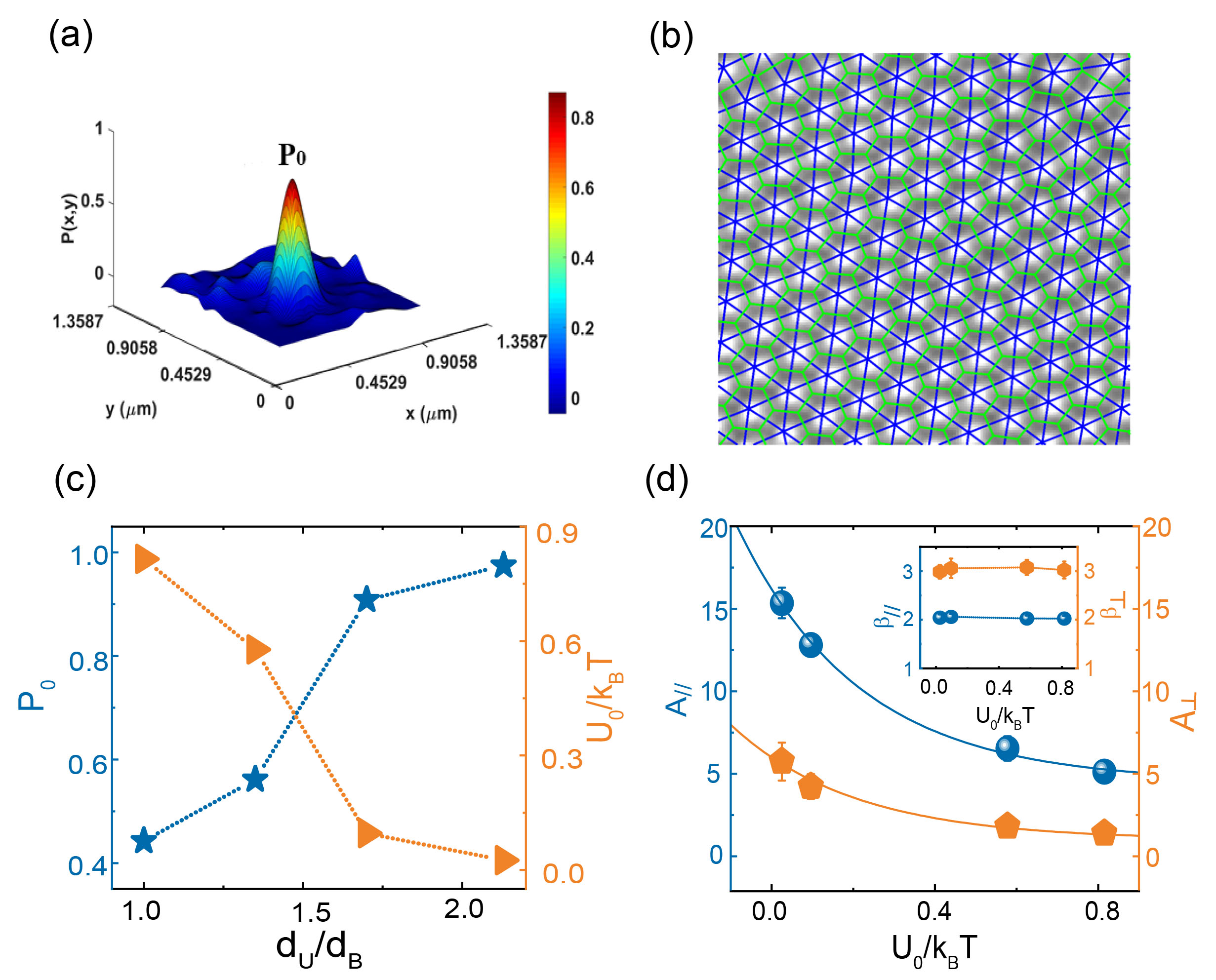
摘要:Using optical microscopy and multiparticle tracking techniques, we investigate the correlated diffusion of colloidal particles over a rugged surface. Our findings demonstrate that the correlated diffusion caused by the hydrodynamic interactions of particles confined to energy landscapes displays a distinctive power-law behavior. The local energy landscape on the rugged surface reduces the long-range hydrodynamic interactions between colloidal particles. The energy landscape influences the strength of hydrodynamic interactions, but not their power-law form. The responding factor of the colloidal particles over the energy landscape to hydrodynamics decays exponentially with the potential energy minimum. We propose a scaling method, with which the correlated diffusion of colloidal particles over various energy landscapes can be scaled onto a master curve. The master curve characterizes the response of the particles over the energy landscape to the hydrodynamics. The scale factors used for the master curve allow for the calculation of the energy landscape. The findings provide physical insights into the confinement hydrodynamics and would be helpful for designing material surfaces and controlling the motion of particles on rough surfaces.
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:057113
卷号:35
期号:5
页面范围:057113
是否译文:否
发表时间:2023-05-10
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0147174
